When it comes to optimizing health, the gut is often overlooked, yet it plays a central role in everything from digestion to mental clarity. As a biohacker, I know how crucial it is to fine-tune the body’s systems, and the gut is no exception. A well-balanced gut microbiome can unlock better energy, sharper focus, and even a stronger immune system.
The good news? There are simple, science-backed ways to give your gut the support it needs. Whether you’re just starting your biohacking journey or you’re a seasoned pro, understanding the right tools and habits can make all the difference. Let’s dive into the key gut health boosters that every biohacker should have on their radar.
Why Gut Health Matters for Biohackers
- Gut health plays a key role in optimizing physical and cognitive performance, which are core objectives for biohackers. The gut, often called the “second brain,” directly interacts with the central nervous system through the gut-brain axis. This connection impacts mood, focus, and mental clarity.
- A balanced gut microbiome supports effective nutrient absorption. Without proper nutrient uptake, energy levels and stamina can decline, limiting the ability to meet biohacking goals. Additionally, the gut produces 70% of the body’s serotonin, influencing mood regulation and overall mental well-being.
- Immune health is tightly linked to the gut. Approximately 70% of the immune system resides in the gastrointestinal tract. Strengthening the gut’s microbiota helps protect against pathogens and reduces inflammation, essential for maintaining peak physical condition.
- The gut also affects metabolic processes, supporting healthy weight management. For biohackers who rely on precise protocols, an optimized gut increases the effectiveness of dietary strategies and personalized nutrition plans.
- Understanding these connections enables biohackers to make informed decisions about habits and interventions aimed at enhancing gut health.
Top Gut Health Boosters Every Biohacker Should Know

Optimizing gut health enhances physical performance and mental clarity. These scientifically-backed boosters provide effective tools for any biohacker aiming to elevate health outcomes.
Probiotics and Their Benefits
Probiotics increase beneficial bacteria in the gut, improving digestion and nutrient absorption. Strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum support immunity and reduce inflammation. Consuming probiotic supplements or fermented foods such as yogurt or kefir provides consistent results.
Prebiotics for a Balanced Microbiome
Prebiotics feed beneficial bacteria and promote microbiome diversity. Foods like:
- garlic
- onions
- bananas
ontain potent prebiotic fibers like inulin. Incorporating prebiotics strengthens gut ecology and enhances probiotics’ effectiveness.
Fermented Foods: Nature’s Gut Healers
Fermented foods contribute live cultures and improve gut microbiota composition. Kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso deliver critical enzymes and probiotics, supporting digestion and immune health. Regular consumption aids microbiome diversity.
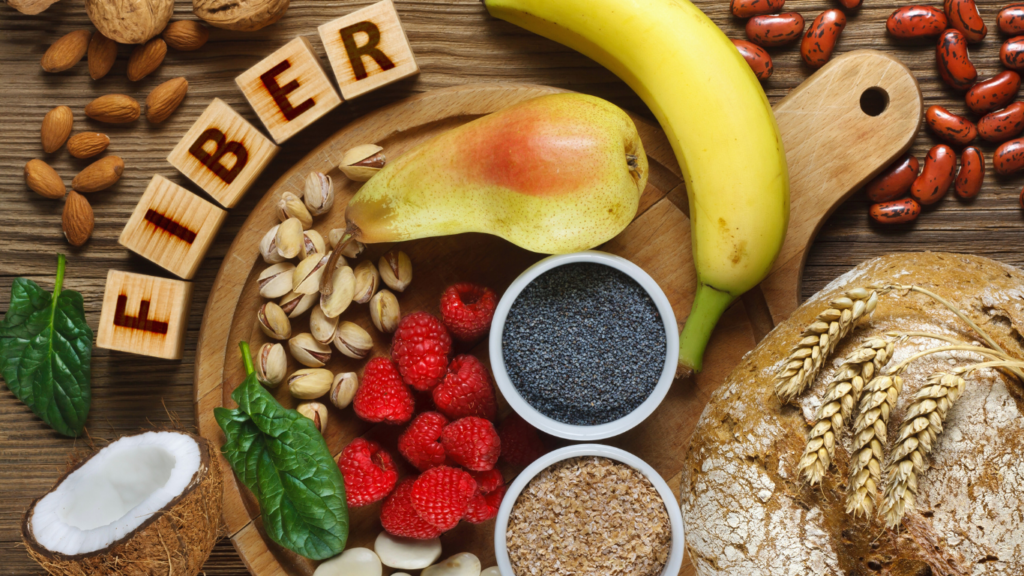
Fiber-Rich Foods and Gut Health
Fiber regulates bowel movements and serves as fuel for gut bacteria. Soluble fibers, found in oats and legumes, produce short-chain fatty acids, fostering gut lining integrity. Insoluble fibers in whole grains and vegetables aid digestion consistency.
The Role of Bone Broth in Gut Repair
Bone broth contains amino acids like glutamine that repair intestinal lining. Collagen and gelatin soothe gut walls and reduce inflammation. Adding bone broth to meals supports recovery from gut damage and improves nutrient absorption.
Lifestyle Habits to Support Gut Health
Incorporating specific lifestyle habits can significantly enhance gut health. These habits work synergistically with diet and supplements, forming the foundation of a balanced microbiome.
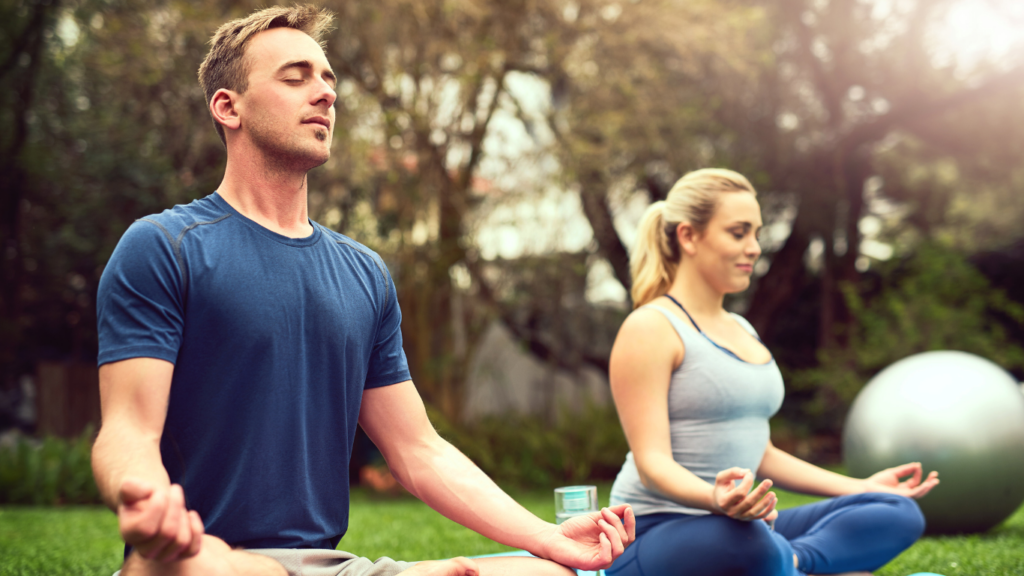
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress alters the gut microbiota composition and increases intestinal permeability. Practicing mindfulness, meditation, and breathing exercises reduces the harmful effects of stress on the gut. Scheduling brief pauses during work hours, dedicating 10-15 minutes daily to relaxation methods, or engaging in activities like yoga can support stress reduction. Studies confirm that a lower stress response correlates with improved gut bacterial diversity.
Importance of Quality Sleep
Poor sleep disrupts gut microbiota balance, while consistent, restorative sleep allows the gut to repair and maintain its function. Sleeping for 7-9 hours nightly improves microbial diversity and optimizes the gut-brain axis. Limiting caffeine intake in the evening, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and using blackout curtains enhance sleep quality. Research indicates that individuals with regular sleep patterns have healthier gut profiles.
Regular Physical Activity and Its Impact
Moderate exercise promotes gut microbiome diversity and enhances digestion. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or strength training improve gut motility and decrease inflammation. Adults should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly to support optimal gut health. Evidence suggests that physically active individuals possess a microbiome better suited for nutrient metabolism and immune support.
Supplements for Optimized Gut Health
Using targeted supplements can accelerate gut optimization by addressing specific microbiome needs. Each supplement provides distinct benefits for digestion, inflammation, and overall gut environment balance.
Digestive Enzymes
Digestive enzymes enhance nutrient breakdown and absorption, supporting optimal gut function. These enzymes, including protease, amylase, and lipase, help digest proteins, carbohydrates, and fats more effectively. Taking enzyme supplements before meals benefits individuals with bloating, gas, or food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance. Supporting the digestive process ensures reduced strain on the gut and better nutrient bioavailability.
Glutamine and Gut Lining Support
Glutamine strengthens the gut lining by fueling intestinal cells and reducing permeability issues. Leaky gut syndrome symptoms, like inflammation or nutrient malabsorption, often improve with glutamine supplementation. Studies show that 5-10 grams of glutamine daily can aid gut repair, making it vital for biohackers aiming to optimize gut health. Balanced gut lining integrity minimizes harmful microbial entry and systemic inflammation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Gut Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce gut-related inflammation by modulating immune responses in the gastrointestinal tract. EPA and DHA, found in fish oil, combat inflammatory conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Research highlights daily doses of 1-2 grams as beneficial for gut inflammation management. Omega-3 supplementation also enhances microbial diversity, contributing to long-term gut and systemic health.